Outline
With TGrid, you can call remote system's nested functions as if they are local functions.
Such remote procedure calling concept is called as RPC (Remote Procedure Call) in the development world, but it contains not only remote function call, but also contains Object Oriented Network. However, in here chapter, we will focus only on the remote nested function calls.
Let's learn how to call remote nested functions with TGrid.
Demonstration
You can run the example program on Playground Website (opens in a new tab), or local machine.
git clone https://github.com/samchon/tgrid.example.remote-object-call
npm install
npm startClient Program
import { Driver, WebSocketConnector } from "tgrid";
import { ICalcConfig } from "./interfaces/ICalcConfig";
import { ICalcEvent } from "./interfaces/ICalcEvent";
import { ICalcEventListener } from "./interfaces/ICalcEventListener";
import { ICompositeCalculator } from "./interfaces/ICompositeCalculator";
export const webSocketClientMain = async () => {
const stack: ICalcEvent[] = [];
const listener: ICalcEventListener = {
on: (evt: ICalcEvent) => stack.push(evt),
};
const connector: WebSocketConnector<
ICalcConfig,
ICalcEventListener,
ICompositeCalculator
> = new WebSocketConnector(
{ precision: 2 }, // header
listener, // provider for remote server
);
await connector.connect("ws://127.0.0.1:37000");
const remote: Driver<ICompositeCalculator> = connector.getDriver();
console.log(
await remote.plus(10, 20), // returns 30
await remote.multiplies(3, 4), // returns 12
await remote.divides(5, 3), // returns 1.67
await remote.scientific.sqrt(2), // returns 1.41
await remote.statistics.mean(1, 3, 9), // returns 4.33
);
await connector.close();
console.log(stack);
};Terminal$ npm start 30 12 1.67 1.41 4.33 [ { type: 'plus', input: [ 10, 20 ], output: 30 }, { type: 'multiplies', input: [ 3, 4 ], output: 12 }, { type: 'divides', input: [ 5, 3 ], output: 1.67 }, { type: 'sqrt', input: [ 2 ], output: 1.41 }, { type: 'mean', input: [ 1, 3, 9 ], output: 4.33 } ]
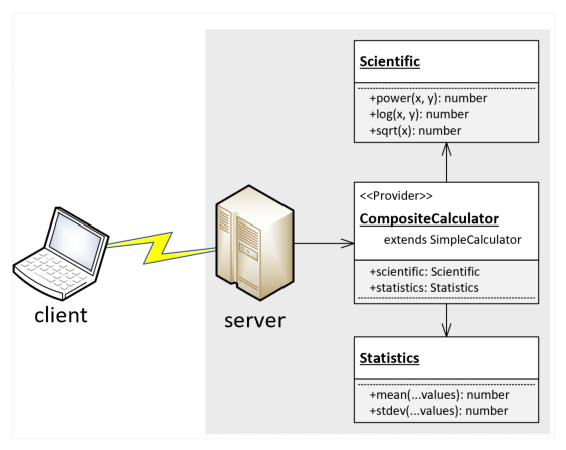
Here is an example websocket client program, calling remote calculator of the websocket server's own.
As you can see, the client has constructed a WebSocketConnector instance with the Header and listener objects. The header object represents a Header component which be directly delivered to the remote system when connecting. The listener object is a Provider component provided for the remote websocket server. It means that, the "Client Program" configures the header value to precision: 2, and provides ICalcEventListener for the remote "Server Program".
After that, you can find out the "Client Program" is calling the remote calculator's function of "Server Program" through Driver<ICompositeCalculator> typed instance. In the remote function call statements, there is one thing important. It is Driver<ICompositeCalculator> type supports nested object's function calls.
This is the "Remote Object Call".
Server Program
import { Driver, WebSocketServer } from "tgrid";
import { ICalcConfig } from "./interfaces/ICalcConfig";
import { ICalcEventListener } from "./interfaces/ICalcEventListener";
import { CompositeCalculator } from "./providers/CompositeCalculator";
export const webSocketServerMain = async () => {
const server: WebSocketServer<
ICalcConfig,
CompositeCalculator,
ICalcEventListener
> = new WebSocketServer();
await server.open(37_000, async (acceptor) => {
const config: ICalcConfig = acceptor.header;
const listener: Driver<ICalcEventListener> = acceptor.getDriver();
const provider: CompositeCalculator = new CompositeCalculator(config, listener);
await acceptor.accept(provider); // ACCEPT CONNECTION
acceptor.ping(15_000); // PING REPEATEDLY TO KEEP CONNECTION
});
return server;
};The "Server Program" is providing CompositeCalculator class to the websocket client.
By the way, when composing the CompositeCalculator class instance as a Provider, you can find out that it is delivering the Header and Driver<ICalcEventListener> typed instances to the construction parameter. By getting the Header value from the "Client Program", "Server Program" configures precision level of the calculator.
Also, if you click the second Providers tab, you can find out that calculators are reporting their calculator operations to the "Client Program" through the Driver<ICalcEventListener> object. Therefore, whenever the calculator function be called, "Server Program" calls remote function of the "Client Program" for event reporting.
Such two-way remote functions providing and header for initialization, this is the "Remote Object Call".
Next Chapter
Until this chapter, we've learned only about simple structured network systems. Complexity has only come to the Provider level, and the network systems were always monotonous. Only single type of server and client were existed.
By the way, TGrid has said that it is useful for developing complicated network system like grid computing in the README (opens in a new tab) and index page of guide documents. At the next chapter, we will learn about the complicated network system.
import { Driver, WorkerConnector, WorkerServer } from "tgrid";
import { ICalcConfig } from "./interfaces/ICalcConfig";
import { ICalcEventListener } from "./interfaces/ICalcEventListener";
import { IScientificCalculator } from "./interfaces/IScientificCalculator";
import { IStatisticsCalculator } from "./interfaces/IStatisticsCalculator";
import { SimpleCalculator } from "./providers/SimpleCalculator";
const EXTENSION = __filename.endsWith(".ts") ? "ts" : "js";
/// `CompositeCalculator` has two additional properties
///
/// - `scientific` from remote worker server
/// - `statistics` from remote worker server
class CompositeCalculator extends SimpleCalculator {
public readonly scientific: Driver<IScientificCalculator>;
public readonly statistics: Driver<IStatisticsCalculator>;
public constructor(props: {
config: ICalcConfig;
listener: Driver<ICalcEventListener>;
scientific: Driver<IScientificCalculator>;
statistics: Driver<IStatisticsCalculator>;
}) {
super(props.config, props.listener);
this.scientific = props.scientific;
this.statistics = props.statistics;
}
}
/// connect to remote worker server
const connect = async <T extends object>(
header: ICalcConfig,
listener: Driver<ICalcEventListener>,
file: string,
): Promise<Driver<T>> => {
const connector: WorkerConnector<ICalcConfig, ICalcEventListener, T> =
new WorkerConnector(header, listener, "process");
await connector.connect(file);
return connector.getDriver();
};
const main = async () => {
const server: WorkerServer<
ICalcConfig,
CompositeCalculator,
ICalcEventListener
> = new WorkerServer();
const config: ICalcConfig = await server.getHeader();
const listener: Driver<ICalcEventListener> = server.getDriver();
// constructor provider combining with remote worker-servers
const provider: CompositeCalculator = new CompositeCalculator({
config,
listener,
scientific: await connect<Driver<IScientificCalculator>>(
config,
listener,
`${__dirname}/scientific.${EXTENSION}`,
),
statistics: await connect<Driver<IStatisticsCalculator>>(
config,
listener,
`${__dirname}/statistics.${EXTENSION}`,
),
});
await server.open(provider);
};
main().catch((exp) => {
console.error(exp);
process.exit(-1);
});